Request Processing
Overview
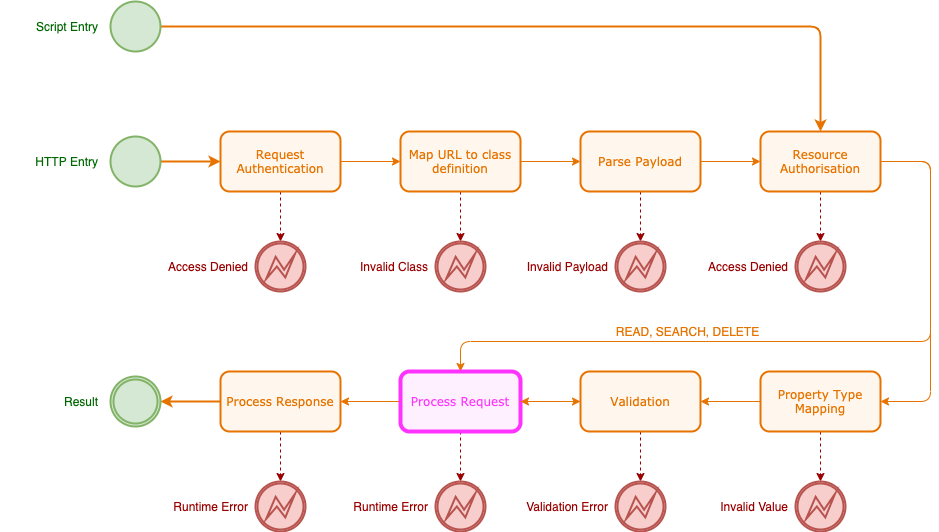
Finally after all the authorisation and validation logic performed in the request so far, the request processing itself can occur. This is where synchronous event scripts and rule scripts are run, object migration is performed and events enqueued.
Precisely what happens within the request processing depends on a number of factors, in particular which operation was requested.
Process Flow
The process flow for all operations can be seen below. Several elements within this flow are shared between operations.
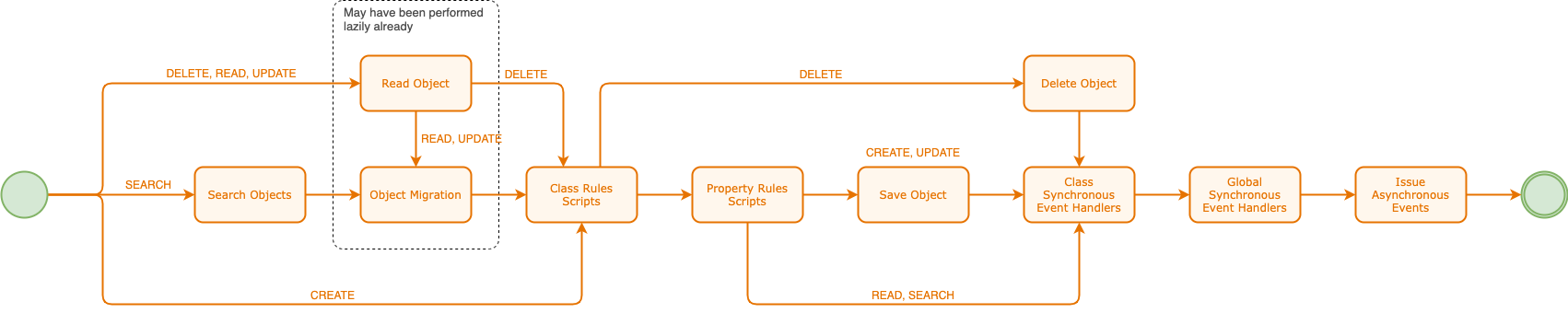
The following table describes the steps used within the request processing and their associated operations.
| Step | Operations | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Search Objects |
SEARCH |
Based on the query being used against the target object, this will return a paged array of the results. The paged format can be seen in operations. |
| Read Object |
READ, UPDATE, DELETE |
The target object may have already been lazy loaded as a result of a read on one of its properties in an access rule. If it hasn’t yet been loaded, it will be loaded here whenever one of the associated operations is used. The read is performed against the store associated with the object’s resource class, which might be an external source. TODO - perhaps bypass this for DELETEs of external objects - because it results in a read and delete |
| Object Migration |
READ, UPDATE, SEARCH |
If the module or application that holds the class definition, or pieces of the class definition for the target object, has been updated beyond the version of the object in storage, the object may need to undergo a migration to get it up to date. See class migration for more information. When object migration is invoked on search results, it is invoked on all entries of the results in the page being returned one by one. |
| Class Rules Scripts |
CREATE, READ, UPDATE, DELETE, SEARCH |
Class rules scripts are run depending on whether their selectors select them. These scripts are run one by one, but they are not guaranteed to run in the order that they are presented in the class definition. In the case of SEARCH operations, the class rules scripts are run for each object returned in the paged results. See rules for more information. |
| Property Rules Scripts |
CREATE, READ, UPDATE, SEARCH |
Like class rules scripts, property rules scripts are run depending on whether their selectors select them. These scripts are run one by one, but they are not guaranteed to run in the order that they are presented in the class definition. See rules for more information. An important difference between class rules scripts and property rules scripts is that class rules scripts are run every time the operation occurs, but property rules scripts are not necessarily run every time for the operation as defined below.
|
| Save Object |
CREATE, UPDATE |
Resource objects are saved if they have been modified or if they are newly created. TODO - what about modifications to objects after this?? - maybe a second save?? |
| Delete Object |
DELETE |
Delete is invoked for DELETE operations only. However, it is possible that a DELETE operation will be triggered from an UPDATE operation or a higher-level DELETE operation. In the case of the delete of a target object, any child resource objects that exist for it also need to be deleted. These child objects are deleted asynchronously. Their class and property access rules are not run in this instance as the delete of these children cannot be stopped, however, the reset of the request flow is run as though the delete of the child was invoked directly. In the case of an update of the target object, if the update causes a child resource to be removed, it is deleted asynchronously with the same processing as above. |
| Class and Global Synchronous Event Handlers |
CREATE, READ, UPDATE, DELETE, SEARCH |
Synchronous class and global event handlers are run near the end of the request processing. These are similar to class rules scripts except that they trigger on either built in events, which are linked to resource object operations, or custom events, which are raised within scripts. |
| Issue Asynchronous Events |
CREATE, READ, UPDATE, DELETE, SEARCH |
The final step in request processing is the issuing of asynchronous resource object events. While these events are raised internally at this point, it is still possible that they are prevented because the entire request flow is transactionalised and an error in response processing could cause the entire request flow changes to be rolled back. |